Understanding the Differences Between Microsuction Ear Wax Removal and Irrigation
Earwax, also known as cerumen, is a natural substance produced by glands in the ear canal. It helps to protect and lubricate the ear, preventing dust, bacteria, and foreign particles from entering the delicate inner ear. However, excessive buildup of earwax can lead to discomfort, impaired hearing, tinnitus and even infection. That’s where ear wax removal comes into play.
There are various methods available for removing excess earwax, including softening drops, microsuction and irrigation. In this article, we will delve into the differences between microsuction and other techniques, highlighting their pros and cons.
Microsuction Ear Wax Removal: An Overview
Microsuction is a gentle and safe method of earwax removal performed by healthcare professionals. It involves using a microscope and a suction device to carefully remove earwax. Microsuction is known for its precision and is suitable for individuals with sensitive ears or a history of ear infections. This method is highly recommended for those with perforated eardrums or ear tubes. This method is typically performed by a healthcare professional, such as an audiologist or an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist. Let’s explore the benefits and drawbacks of this technique.
Advantages of Microsuction Ear Wax Removal
- Microsuction is a specialised technique that utilises a microscope and a suction device to remove earwax. This method offers a high level of precision, allowing healthcare professionals to visualise and extract the earwax effectively.
- Individuals with sensitive ears or a history of ear infections can benefit from microsuction as it minimises the risk of discomfort or damage. The use of a microscope ensures that the healthcare professional can accurately target and remove the excess earwax without causing harm to the delicate structures of the ear.
- Microsuction is particularly recommended for individuals with perforated eardrums or those with ear tubes, as it provides a safe and controlled method of earwax removal. Healthcare professionals who specialise in this technique can offer personalized guidance based on individual circumstances.
- When earwax becomes impacted or hard, over-the-counter remedies may not be sufficient. Microsuction ear wax removal offers a more effective solution in such cases ensuring optimal ear health.
- Unlike some other methods, by directly removing the excess ear wax with microsuction individuals often notice immediate relief from symptoms associated with excessive earwax, such as hearing loss or earache. Prompt relief from symptoms is especially beneficial for individuals who rely heavily on their hearing, such as musicians, performers, or individuals working in professions that require clear hearing. Microsuction ear wax removal ensures minimal disruption to their daily activities.
Disadvantages of Microsuction Ear Wax Removal
- Professional Assistance Required: Microsuction ear wax removal should only be performed by a trained healthcare professional. Healthcare professionals who specialise in ear care, such as audiologists or ENT specialists, have the necessary expertise and experience to perform the procedure safely. Attempting to remove earwax at home with instruments can be risky and may damage the delicate structures of the ear.
- Potential for Infection: If the instruments used are not properly sterilised or if the procedure is not carried out under sterile conditions, there is a risk of infection. Healthcare professionals take precautions to ensure that the instruments used are either single use or sterilised before each procedure.
- Complications of ear wax removal with microsuction are uncommon. However, possible complications, side-effects and material risks inherent in the procedure include but are not limited to: incomplete removal of ear wax requiring a return visit (for severely impacted wax, or insufficiently softened wax), dizziness, minor bleeding, discomfort, ringing in the ear (tinnitus), perforation of the ear drum and hearing loss.
- Discomfort or Pain: Some individuals may experience discomfort or pain during manual microsuction ear wax removal, particularly if the wax is impacted or if there is an underlying ear infection. The sensation of discomfort or pain during manual instrument ear wax removal can vary from person to person but is usually minimal. Factors such as the individual’s pain tolerance, the condition of the earwax, and the presence of any underlying ear infections can contribute to varying levels of discomfort. To ensure the risk of complications is minimised, it is essential that the ear wax is softened for at least 3 days, at least twice a day with Earol spray. This has been shown in a clinical study to reduce the risk of dizziness and discomfort. It significantly reduces the chance of spiky, hard ear wax scratching the walls of the ear canal as it is removed, and greatly increases the chances of a successful procedure.
Alternatives to Microsuction Ear Wax Removal
While microsuction ear wax removal is a common and effective method, it is important to explore other alternatives that may be better suited to individual needs and preferences.
1. Earwax Softening Drops
Earwax softening drops are over-the-counter solutions that help to soften and loosen earwax. These drops typically contain hydrogen peroxide, sodium bicarbonate, or olive oil as active ingredients. Earwax softening drops are a convenient option for individuals who prefer self-care and want to address mild cases of earwax buildup at home. These drops work by breaking down the earwax, making it easier to come out naturally. However, they are not as effective for impacted earwax and come with their own risks.
- Peroxide Drops: At Hearing First we strongly advise against the use of peroxide-based ear drops. While many people can use them without any harm, we see a significant number of patients with severe sensitivity to the peroxide ingredient. In these people, the ear canal becomes red and inflamed and the canal skin peels off just like a severe sunburn. This will make the skin sore and can make the microsuction wax removal process very uncomfortable.
- Bicarbonate Drops: While many people can use sodium bicarbonate drops without any harm, we see a significant number of patients with a sensitivity to the active ingredient. This can occur especially when the drops are used for more than the recommended 5 days, or where the patient has dry skin.The ear canal surface is meant to be acidic in order to prevent the growth of bacteria. Sodium bicarbonate is alkaline, and reduces the acidity of the ear canal surface. In many instances, excessive sodium bicarbonate use can lead to peeling skin and/or bacterial infection of the ear canal. This will make the skin sore and can make the microsuction wax removal process very uncomfortable.
- Olive Oil: While many people can use kitchen olive oil without any harm, we see a significant number of patients with ear infections caused by contaminants in the oil. Surprisingly, this is more likely with Extra Virgin olive oil, as it has not been heat treated and filtered – this leaves all the beneficial plant nutrients, but potentially can contain bacteria or fungal spores that would normally be killed off by the strong acid in the stomach. The ear canal doesn’t have such strong defences, and this is why we recommend only sterile, pharmacy grade olive oil, particularly Earol, as the spray makes it very easy to apply.
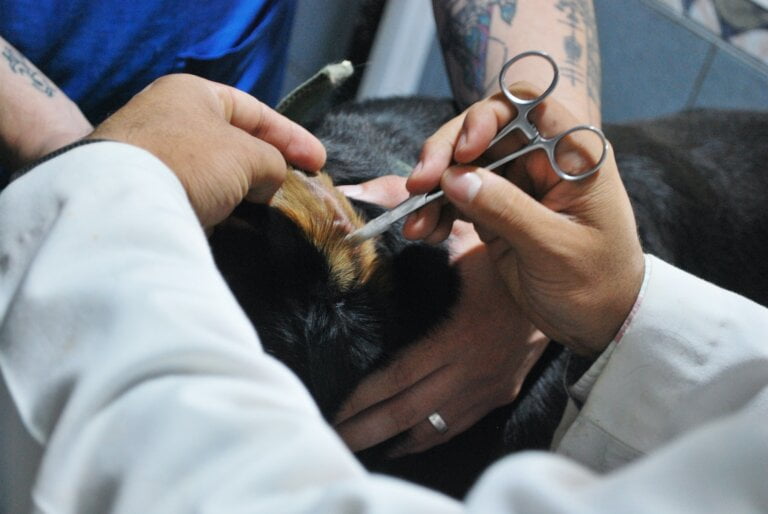
2. Ear Irrigation
Ear irrigation, also known as ear syringing, involves flushing the ear canal with a gentle stream of warm water. This method helps to dislodge and remove earwax. It is typically performed by a healthcare professional using specialised equipment. Ear irrigation can be effective for moderate cases of earwax buildup, but caution must be exercised to ensure proper technique and water temperature due to a higher incidence of complications compared to other methods of ear wax removal such as microsuction.
- Ear irrigation was previously a widely used technique for removing excess earwax. It involves the use of specialised equipment that delivers a controlled flow of warm water into the ear canal, dislodging and flushing out the earwax.
- Due to the pressure of water applied to the ear canal, it is important to ensure that the procedure is performed by a trained healthcare professional to minimise the risk of injury or infection.
- Correct technique and appropriate water temperature are crucial during ear irrigation to prevent any potential complications. Healthcare professionals have the knowledge and experience to perform the procedure safely, ensuring optimal results.
- Complications may include infection, perforation (rupture) of the ear drum, tinnitus, pain, bruising, bleeding and hearing loss. This is why at Hearing First we never syringe.
Conclusion
When it comes to earwax removal, microsuction ear wax removal is an effective and reliable method, especially for stubborn or impacted wax. However, it is crucial to seek professional assistance to ensure the procedure is performed safely and without complications. Alternatives such as earwax softening drops or ear irrigation may also be considered depending on individual circumstances. It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable method for your specific situation. Prioritise your ear health and seek prompt attention to maintain optimal hearing and prevent potential complications.