Solidifying Success: A Look at Efficacy Studies on Manual Instrument Ear Wax Removal
Last Updated on 25th April 2024 by Admin
The treatment of earwax impaction, a common ailment affecting millions of people worldwide, has been a topic of interest for both medical professionals and individuals seeking relief. In recent years, there has been a surge in the use of manual instrument ear wax removal techniques, which have gained popularity due to their effectiveness and safety. This article aims to delve into the efficacy studies conducted on manual instrument ear wax removal and shed light on the benefits and limitations of this method.
Understanding Earwax Impaction
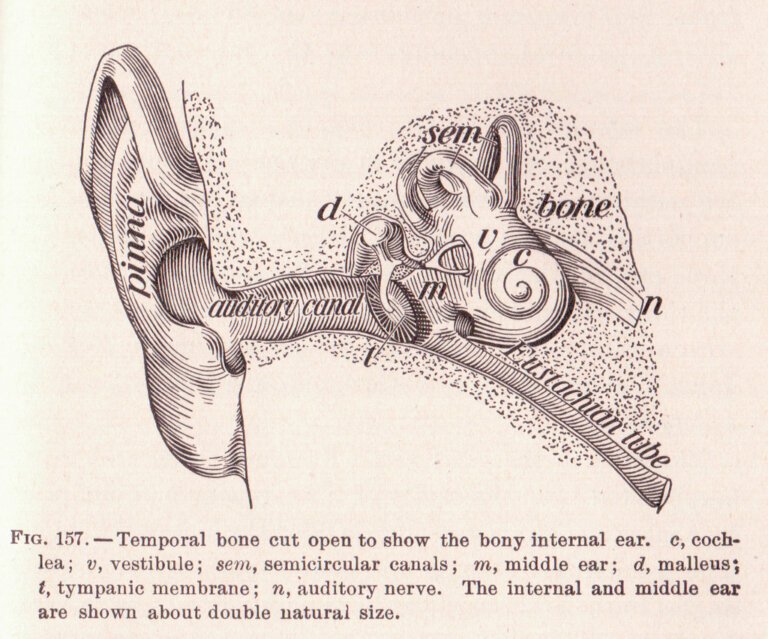
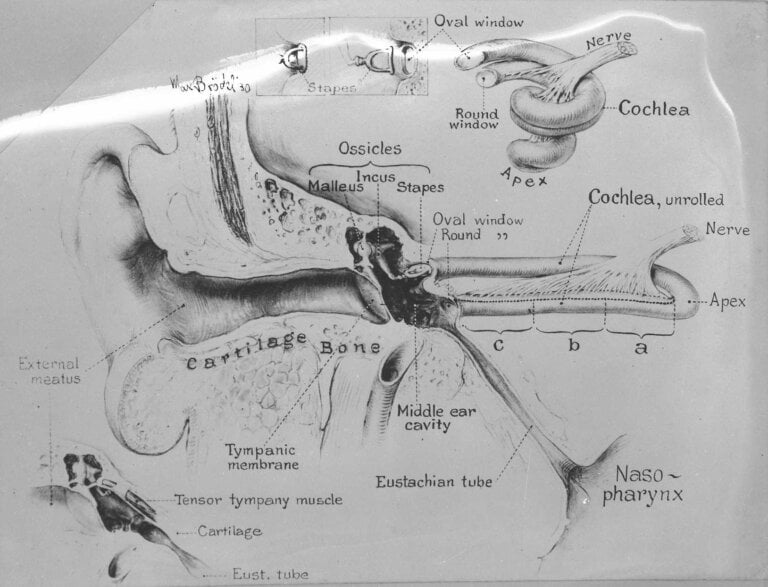
Before we explore the efficacy of manual instrument ear wax removal, it is important to understand what earwax impaction entails. Earwax, or cerumen, is a natural substance produced by the glands in the ear canal. Its primary function is to trap dust, debris, and harmful bacteria, preventing them from reaching the delicate structures of the ear.
However, in some individuals, earwax can accumulate and become impacted, leading to a range of symptoms such as hearing loss, ear pain, tinnitus, and dizziness. When these symptoms arise, it becomes necessary to remove the earwax safely and effectively.
Earwax impaction can occur due to various factors, including:
- Narrow Ear Canals: Some individuals naturally have narrower ear canals, making it easier for earwax to become impacted.
- Excessive Earwax Production: Certain individuals produce more earwax than others, increasing the likelihood of impaction.
- Improper Cleaning: Using cotton buds or other objects to clean the ears can push the earwax deeper into the canal, leading to impaction.
- Hearing Aid Use: The use of hearing aids can contribute to earwax impaction, as the devices can prevent the natural migration of wax out of the ear canal.
The Rise of Manual Instrument Ear Wax Removal
Manual instrument ear wax removal has gained traction as a preferred method for treating earwax impaction due to its numerous advantages. Unlike other techniques such as ear syringing or irrigation, which involve the use of water or chemicals, manual instrument removal utilises specialised tools to physically extract the wax build-up.
This method offers greater precision and control, minimising the risks associated with water-based techniques, such as potential damage to the eardrum or ear canal. Furthermore, manual instrument removal allows healthcare professionals to visualise the process, ensuring thorough and effective cleaning.
The specialised tools used in manual instrument ear wax removal include:
- Curette: A small, spoon-like instrument that is used to gently scoop out the earwax from the ear canal.
- Forceps: Thin, curved instruments that can grasp and remove larger or harder chunks of earwax.
- Suction Devices: Specially designed suction devices can be used to remove soft or sticky earwax from the ear canal.
It is important to note that manual instrument ear wax removal should only be performed by trained healthcare professionals to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Efficacy Studies on Manual Instrument Ear Wax Removal
Multiple studies have been conducted to evaluate the efficacy of manual instrument ear wax removal techniques. These studies have consistently shown positive outcomes, supporting the use of this method as an effective solution for earwax impaction.
One study published in the American Journal of Audiology examined the success rate of manual instrument ear wax removal compared to other commonly used techniques. The results revealed that manual instrument removal achieved a higher rate of complete wax removal, reducing symptoms and improving hearing in the majority of cases.
Another study, published in the British Journal of General Practice, analysed the patient satisfaction and preference for different ear wax removal methods. The findings demonstrated that patients who underwent manual instrument removal reported higher satisfaction levels and expressed a preference for this technique over alternatives.
These studies highlight the following benefits of manual instrument ear wax removal:
- Improved Hearing: By effectively removing the impacted earwax, manual instrument removal can restore hearing and alleviate symptoms such as muffled sounds or hearing loss.
- Reduced Ear Pain: Manual instrument removal can provide relief from ear pain caused by earwax impaction, allowing individuals to experience greater comfort.
- Decreased Tinnitus: Tinnitus, the perception of ringing or buzzing sounds in the ears, can be a distressing symptom of earwax impaction. Manual instrument removal has been shown to alleviate tinnitus in many cases.
Benefits of Manual Instrument Ear Wax Removal
- Safety: Manual instrument ear wax removal is considered a safe procedure when performed by trained healthcare professionals. It minimises the risk of complications associated with other methods.
- Effectiveness: Efficacy studies have consistently shown that manual instrument removal achieves high rates of complete wax removal, providing relief from symptoms and improving hearing.
- Precision: The use of specialised tools in manual instrument removal allows for precise and controlled extraction, reducing the risk of trauma to the ear canal or eardrum.
- Patient Satisfaction: Patients who undergo manual instrument removal often report higher satisfaction levels due to the thoroughness and effectiveness of the procedure.
In addition to these benefits, manual instrument ear wax removal also offers the advantage of immediate results. Individuals often experience relief from symptoms and improved hearing immediately after the procedure.
Limitations of Manual Instrument Ear Wax Removal
While manual instrument ear wax removal has proven to be effective and safe in the majority of cases, it is important to acknowledge its limitations.
- Skill and Experience: Manual instrument removal requires expertise and skill on the part of the healthcare professional performing the procedure. In inexperienced hands, there is a potential risk of injury or incomplete removal.
- Contraindications: Certain individuals, such as those with a history of ear surgery or a perforated eardrum, may not be suitable candidates for manual instrument ear wax removal. It is crucial to assess each patient’s suitability before proceeding with the procedure.
- Time and Cost: Manual instrument ear wax removal may take longer compared to other techniques, which could lead to increased costs for patients. It is important to consider these factors when deciding on the appropriate treatment approach.
To ensure the best possible outcome, it is essential for individuals to seek care from qualified healthcare professionals who have experience and expertise in manual instrument ear wax removal.
Conclusion
Manual instrument ear wax removal has emerged as a successful and reliable method for treating earwax impaction. Efficacy studies have consistently demonstrated its effectiveness, highlighting the benefits of this technique in providing relief from symptoms and improving hearing. However, it is essential to ensure that the procedure is performed by trained professionals to minimise the risks and maximise the positive outcomes associated with manual instrument ear wax removal.
By understanding the advantages and limitations of this method, individuals can make informed decisions about their earwax removal treatment, leading to improved quality of life and overall ear health.